What Parts of a Cow are Not Used : Maximizing Meat Yield
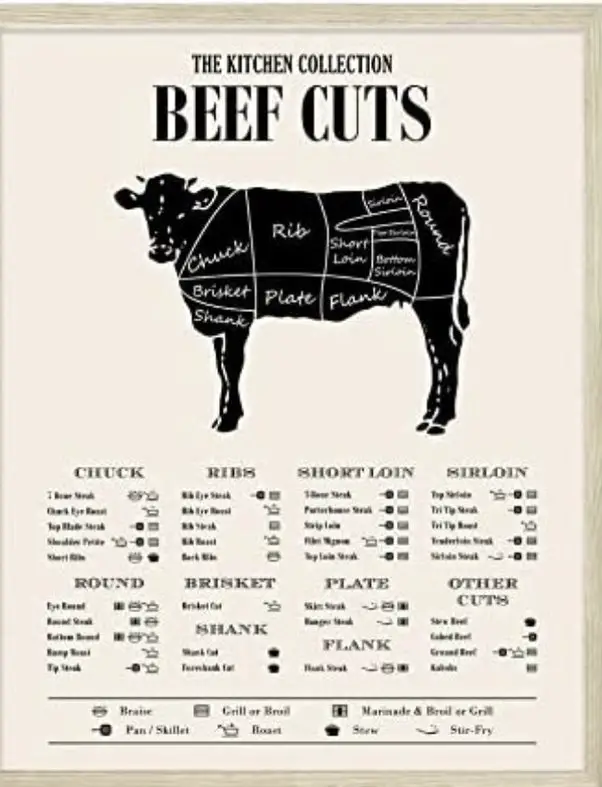
Some parts of a cow that are not used for consumption include the hide, hooves, and skeletal structure. These by-products are less favorable for human consumption but can be utilized for other purposes.
Cows provide a variety of products beyond their meat, such as leather from the hide, gelatin from the bones and hooves, and insulin from the pancreas. While most parts of the cow are utilized in some way, certain components like the hide and skeletal structure are not commonly consumed by humans.
Understanding the various uses of different cow parts sheds light on the resourcefulness and efficiency in utilizing the entirety of these animals in various industries.
Edible Parts Of A Cow
Muscle Meat: The muscle meat of a cow, including cuts like steaks and roasts, is commonly consumed and is a significant source of protein in many diets.
Organ Meat: Organs such as the liver, kidneys, and heart are also used for consumption, providing essential nutrients and flavors in various cuisines.
Tongue and Tail: The tongue and tail of a cow are considered delicacies in some cultures and are utilized as food products, adding diversity to culinary traditions.
Bone Marrow: Bone marrow, often extracted from cow bones, is utilized as a rich and flavorsome ingredient in cooking, offering nutritional benefits.
Non-edible Parts Of A Cow
Hide and skin: The hide and skin of a cow are not used for food consumption. However, they are utilized in the production of leather and various leather products.
Horns and hooves: These non-edible parts of the cow are used in the manufacturing of gelatin, adhesives, and other industrial products.
Bones: While not suitable for human consumption, cow bones are utilized in making bone meal, fertilizers, and other industrial applications.
Intestines: The intestines of a cow are not consumed as food but are used in producing sausage casings and other food products.
Blood and other by-products: Non-edible parts such as blood, fats, and organs are processed to make pharmaceuticals, pet food, and other industrial goods.
Uses Of Non-edible Parts
Leather and Other Goods: One of the non-edible parts of a cow, the hide, is used to make leather products such as shoes, belts, and bags. Other parts like horns and bones are utilized in making buttons, combs, and glue.
Fertilizer and Other Agricultural Uses: Non-edible parts such as blood, bone meal, and manure are used as natural fertilizers to enhance soil quality. Additionally, hair and feathers are utilized in making agricultural products like fertilizer.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications: Some non-edible parts of cows, like glands and organs, are used to produce medicines and pharmaceutical products. For instance, insulin is derived from the pancreas of cows, and gelatin is obtained from their bones and connective tissues.

Credit: twitter.com
Sustainable And Ethical Practices
Sustainable and Ethical Practices Reducing waste is an essential part of sustainable and ethical practices in the meat industry. Utilizing by-products such as hide, hooves, and bones ensures that all parts of the cow are used, minimizing waste. This approach aligns with the principles of animal welfare, as it respects the value of every part of the animal and reduces environmental impact. By incorporating these practices, the industry can promote a more sustainable and ethical approach to beef production.
Innovative Solutions For Maximizing Yield
Discover innovative solutions for maximizing yield by exploring the lesser-known parts of a cow that are not typically used for consumption. From hide to hooves, various by-products like skeletal structures offer alternative ways to optimize resource utilization in the beef industry.
Parts of a cow that are not traditionally used for food include the hide, hooves, and skeletal structure. However, these by-products can still be utilized in various industries, such as leather and gelatin production. With new technologies and innovations, even more parts of the cow can be utilized for food production. For example, alternative meat products have been developed using plant-based ingredients and even lab-grown meat cells. These products aim to maximize yield and reduce waste by utilizing parts of the cow that are typically discarded. As consumers become more conscious of their environmental impact, the demand for these innovative solutions is increasing.
Credit: www.ebay.com

Credit: www.amazon.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Part Of The Cow Is Not Eaten?
The moo and the hair are not eaten. Most parts of the cow can be consumed, except for the contents of the digestive and urinary system. The hide is not generally eaten, but it can be if thoroughly cooked. By-products like hide, hooves, and skeletal structure are not favorable for consumption.
What Parts Of A Cow Are Wasted?
Hide, hooves, and skeletal structure are parts of a cow that are not used for food.
Do All Parts Of A Cow Get Used?
Almost all parts of a cow are used, except for the hide, hooves, and skeletal structures. These are less suitable for human consumption.
Do They Use Every Part Of The Cow?
Yes, almost every part of the cow is utilized, except for the hide, hooves, and skeletal structure.
Conclusion
While most parts of a cow are edible, by-products like hide, hooves, and bones are not commonly consumed. Understanding the various uses of different parts is essential for sustainable practices in the meat industry. Proper preparation can make even less favored parts usable.
Also Worth Reading:
- Is Raising Cows Worth It: Maximizing Profitability
- Best Cattle Feed : Top Picks for Healthy Cows
- Best Way to Load Cattle in a Stock Trailer: Expert Tips
- Cattle Problem in Australia: Urgent Solutions
- Discover the Ultimate Best Cattle Feed Formula
- How are Farm Cows Killed : Unveiling the Slaughter Process
- How Do Cows Know Not to Cross Cattle Guards : The Surprising Science
- How Do You Connect Cattle Panels Together: Expert Tips
- How Do You Know If Baby Has Cows Milk Intolerance: Symptoms and Diagnosis.
- How Do You Know If Cows are Pregnant : A Comprehensive Guide



