Why Did the Elephant Cross the Road
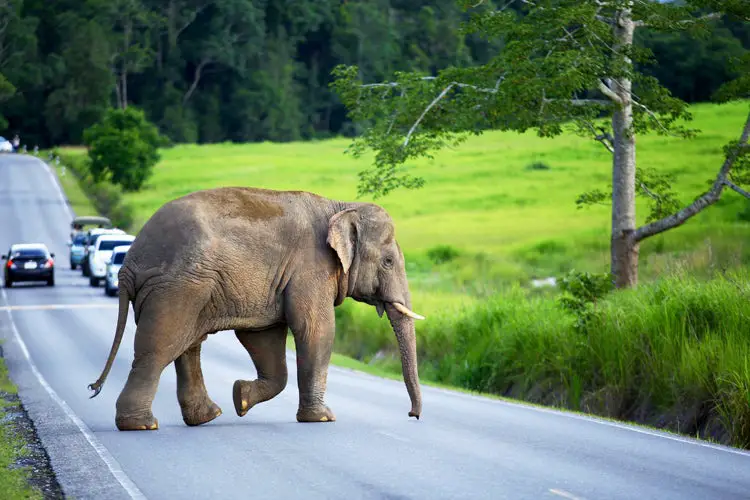

The elephant crossed the road to forage for grass and other plants, but also faced the risk of being hit by speeding cars and poaching. Roads like the East-West Highway in Peninsular Malaysia pose significant challenges for elephants, as they need large home ranges and are attracted to the roadside for food.
To address this issue, researchers from the University of Nottingham in Malaysia are calling for measures such as speed limits, habitat management, and public engagement to modify driver behavior and keep elephants away from the roadside. Their research, published in the journal Biological Conservation, aims to study the management and ecology of Malaysian elephants.

Credit: www.riddles.com
Understanding The Phenomenon
When roads intersect with the habitats of elephants and other wildlife, it can create significant challenges for their movement and behavior. Elephants need large home ranges to fulfill their ecological needs, and the presence of roads can act as a barrier. Additionally, the proximity of roads to elephant habitats can expose them to risks such as poaching and collisions with speeding vehicles. Moreover, roadsides often attract elephants as foraging spots for their preferred food sources. To address these issues, measures such as enforcing speed limits, habitat management, and public engagement to modify driver behavior are crucial. These initiatives aim to mitigate the impact of roads on elephant movement and behavior, promoting landscape connectivity and the conservation of wildlife. The research emphasizes the importance of understanding the complex response of wild elephants to roads to implement effective conservation strategies.
Ecological Reasons
| Foraging for Food Along the Roadside | Seeking Water Sources Across the Road |
| Elephants are attracted to the roadside to forage for their favourite food – grasses and other early succession plants. | The elephant crossed the road to access water sources such as rivers or lakes. |
| For elephants, roads pose a significant barrier as they need very large home ranges to fulfil their ecological needs. | This exposes them to the threat of poaching. |
| Researchers call for a stop to any further expansion of remote highways that lie between wildlife refuges. | They advocate for speed limits and habitat management to keep elephants away from the roadside. |
| Public engagement is also important to modify driver behavior on highways and roads that cut across important wildlife habitats. | This research has been published in the academic journal Biological Conservation. |
Human-induced Factors
Roads like the East-West Highway in Peninsular Malaysia pose huge challenges for elephants, who need large home ranges and are attracted to the roadside for foraging. Additionally, the presence of speeding cars and the risk of poaching make it necessary to implement measures such as speed limits, habitat management, and public engagement to protect elephants and their habitats from the impact of human-induced factors.
| Human-Induced Factors |
| Encounters with Speeding Cars and the Threat of Poaching |
| Elephants face numerous challenges when crossing roads due to human activities. One major concern is encounters with speeding cars, which pose a significant threat to their safety. Elephants are attracted to roadside areas as they often find their favorite food, such as grasses and early succession plants there. Unfortunately, this exposes them to the danger of poaching as well. As a result, there is a pressing need for habitat management and enforcement of speed limits to keep elephants away from the roadside. Experts advocate for the modification of driver behavior through public engagement, particularly on roads that intersect important wildlife habitats. They also call for a halt to the expansion of remote highways like the East-West Highway in Peninsular Malaysia, which cuts through wildlife refuges, and the implementation of measures to ensure the conservation of elephant populations. (134 words) |
| The Need for Habitat Management and Speed Limit Enforcement |
| In order to protect elephants from encounters with speeding cars and minimize the threat of poaching, habitat management is crucial. This involves creating and maintaining suitable habitats for elephants away from busy roads. Additionally, enforcing speed limits can also help reduce the risk of accidents involving elephants. By strictly monitoring and penalizing drivers who exceed the speed limit, there will be a safer environment for both humans and elephants. Public engagement plays a vital role in raising awareness about the importance of wildlife conservation and encouraging responsible driving practices. It is essential to educate the public about the ecological needs of elephants and the potential consequences of their actions. With proper habitat management and speed limit enforcement, we can ensure the well-being and survival of these majestic creatures. (137 words) |

Credit: www.riddles.com
Conservation Efforts
The conservation efforts to protect wildlife are paramount. The calls for halting road expansion in wildlife areas are gaining traction, as it’s recognized that roads pose a significant barrier to the movement of wildlife, particularly elephants. Public engagement and driver education are crucial in modifying driver behavior, enforcing speed limits, and managing habitats to keep wildlife away from roads. Research has emphasized the importance of halting the expansion of remote highways that lie between wildlife refuges and implementing measures to protect wildlife from the threats posed by roads, such as poaching incidents. These efforts are pivotal in preserving the ecological balance and ensuring the safety of wildlife in their natural habitats.
Case Studies
Real-Life Examples of Elephant-Road Interactions:
Roads like the East-West Highway in Peninsular Malaysia pose huge challenges for landscape connectivity and the movement of wildlife. Roads pose a significant barrier for elephants as they need very large home ranges to fulfil their ecological needs. Elephants are also attracted to the roadside to forage for their favourite food – grasses and other early succession plants. As well as speeding cars, this also exposes them to the threat of poaching. Researchers are calling for a stop to any further expansion of this remote highway – which lies between two wildlife refuges – as well as other measures. They want to see the introduction and enforcement of speed limits and habitat management to keep elephants away from the roadside. They are also calling for public engagement to modify driver behaviour on this highway and other roads that cut across important wildlife habitats. Their research has been published in the academic journal Biological Conservation. The work was led by Jamie Wadey as part of MEME – a research project at the University of Nottingham Malaysia Campus studying the Management and Ecology of Malaysian Elephants.
:quality(70)/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/irishtimes/KRM5NHFE57XXLZIJYRHUGDA4BU.jpg)
Credit: www.irishtimes.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Why Did The Elephant Cross The Road
Why Do Elephants Cross Roads?
Elephants cross roads for foraging and habitat needs, but also face threats from speeding cars and poaching. It’s important to manage and enforce speed limits, habitat protection, and public engagement to protect elephants from the hazards of roadside crossings.
Why Did The Elephants Go To The River?
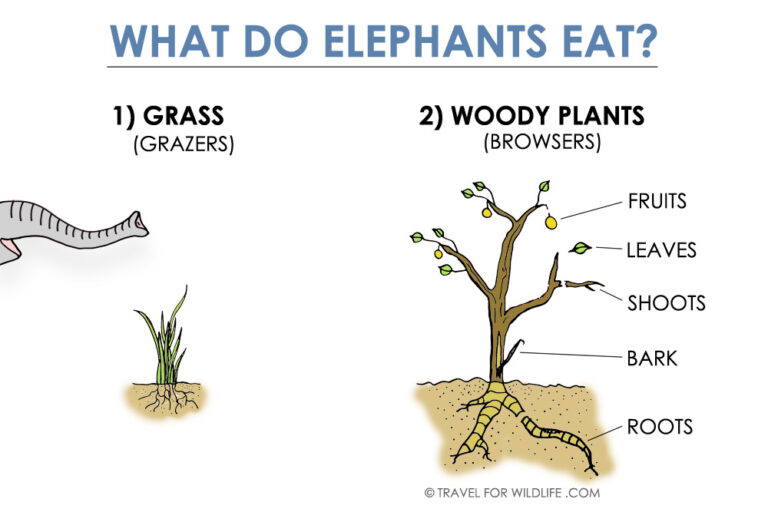
The elephants went to the river to drink water and bathe. They also visited a tailor’s shop along the way to get food. Elephants eat grasses, leaves, shrubs, fruits, and roots. They may also eat woody parts of trees during dry seasons.
What Do Elephants Eat?
Elephants eat grasses, leaves, shrubs, fruits, and roots based on the season and their habitat. In dry conditions, they consume more woody parts like twigs, branches, and barks.
Why Did The Elephant Cross The Road?
The elephant crossed the road because it needed to access its large home range and find its favorite food, like grasses and early succession plants. However, crossing roads exposes elephants to dangers like speeding cars and poaching.
Conclusion
Understanding the reasons behind an elephant crossing the road is crucial for wildlife preservation. The challenges they face, from habitat fragmentation to poaching threats, require collaborative efforts in building safer crossings and enforcing protective measures. By addressing these issues, we can ensure the safety and conservation of these magnificent creatures for future generations.