Are Lions Monogamous

Lions are not monogamous, as they form temporary bonds during mating season and males may change prides throughout their lives. However, they do display strong social bonds and affection towards their like-sexed companions, with females staying with their mothers’ pride or sisters in a new pride and males remaining with their coalition partners.
This behavior increases the chances of successful fertilization and discourages infanticide by males. While feline species like lions or feral cats may stay in groups, mating is not a part of their social structure.

Credit: 12travelafrica.com
Understanding Lion Behavior
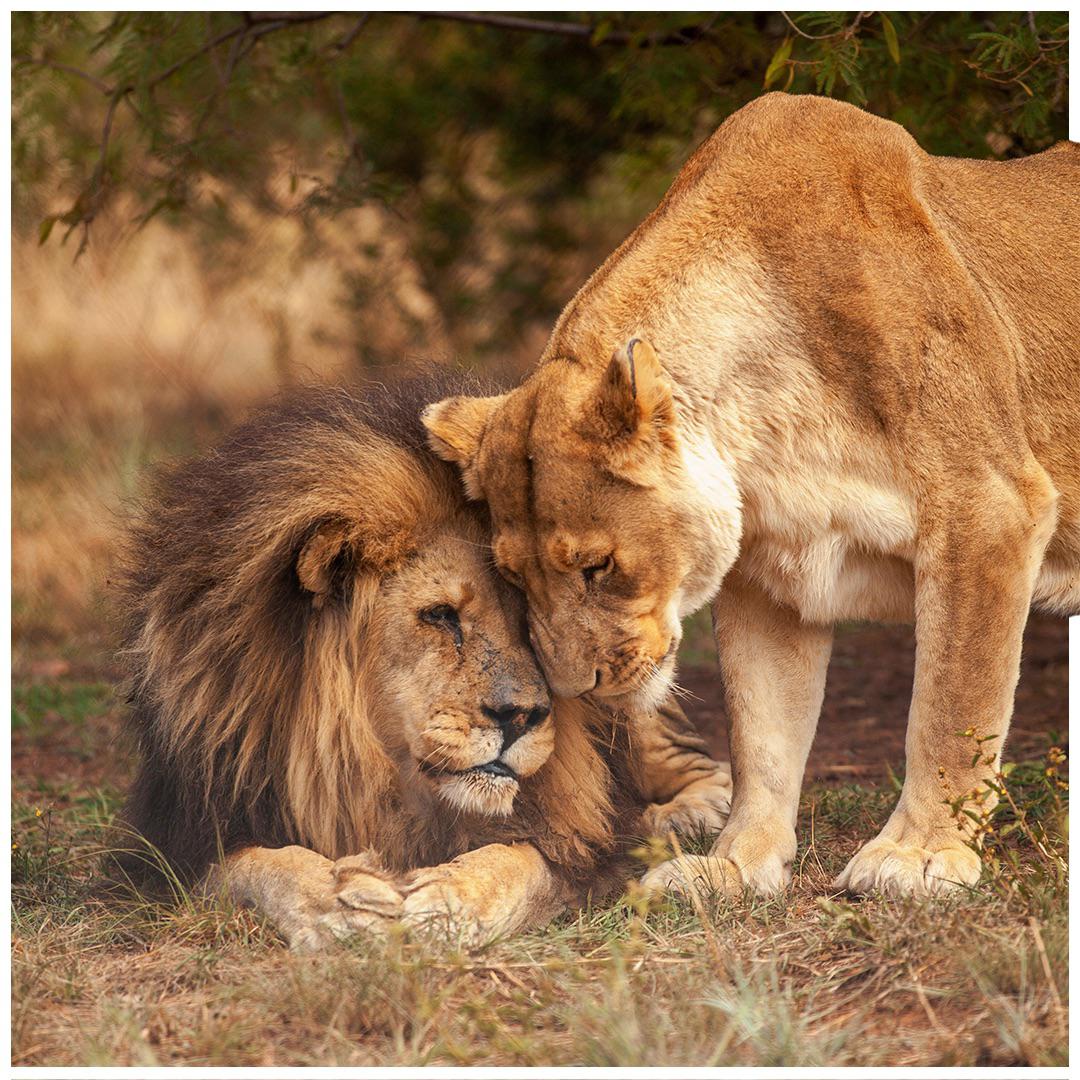
Lions, the majestic creatures of the wild, have a fascinating social structure. Unlike some other animals, lions do not mate for life. Instead, they form temporary bonds during the mating season. Male and female lions venture out together to hunt and provide sustenance not only for themselves but also for the growing young males and female cubs. While the concept of love may not be directly applicable to animals like lions, they do display behaviors that indicate strong social bonds and care for their partners and offspring. Females often spend their lives in their mothers’ pride or with their sisters in a new pride, while males may only spend a few years in a given pride but remain with their coalition partners throughout their lives. This unique social behavior can be attributed to the survival instincts and reproductive strategies of these magnificent creatures.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Monogamy Vs Polygamy
Lions are not monogamous and do not mate for life. While they may form temporary bonds during mating season, they do not have long-term mates like some other animals.
In the animal kingdom, monogamy and polygamy are two different relationship types that can be observed. Lions, for example, are not monogamous creatures. While they do form temporary bonds during the mating season, they do not have mates for life. Female lions may mate with multiple males as a reproductive strategy, increasing the chances of successful fertilization and discouraging infanticide by confusing paternity. In contrast, male lions may form coalitions and remain with their partners throughout their lives. While we may not apply the concept of love directly to animals, lions do display behaviors that indicate strong social bonds and care for their partners and offspring. Understanding different relationship types in the animal kingdom helps us appreciate the diversity of social structures and reproductive strategies.Lion Reproduction
Are lions monogamous? The reproduction and life cycle of lions reveal interesting mating patterns. In captivity, lions often breed every year, while in the wild, they usually breed no more than once in two years. Both male and female lions are polygamous, with females usually restricted to one or two adult males in their pride. Lionesses may mate with multiple males as a reproductive strategy to increase the chances of successful fertilization and discourage infanticide by males. While the concept of love may not be directly applicable to animals, lions do display strong social bonds and care for their partners and offspring. Females spend their lives in their mothers’ pride or with their sisters in a new pride, while males remain with their coalition partners throughout their lives. So, while lions are not monogamous, they form temporary bonds during the mating season.

Credit: www.cherrypickett.com
Are Lions Monogamous?
Understanding the reality of lion’s monogamy is important when it comes to studying their social behavior. While it may be tempting to assume that lions are monogamous creatures, the truth is more complex. Lions do form temporary bonds during the mating season, but they do not mate for life. They can have multiple mates, and lionesses may mate with multiple lions as a reproductive strategy to increase the chances of successful fertilization. Female lions spend their lives in their mothers’ pride or with their sisters in a new pride, while males may only spend a few years in a given pride but remain with their coalition partners throughout their lives.
Comparing Lion Behavior With Other Animals
| Comparing Lion Behavior with Other Animals |
|---|
| Monogamy in the Animal Kingdom |
| Why Lions Take Multiple Sexual Partners |
Lions are not monogamous animals. While some animals mate for life, lions have a different approach to reproduction. Male and female lions form temporary bonds during the mating season. This allows for genetic diversity among the cubs and helps prevent infanticide by males. Lionesses may mate with multiple males, increasing the chances of successful fertilization and confusing paternity. Lions show strong social bonds and care for their partners and offspring, although the concept of love may not be directly applicable to animals. Females spend their lives in their mothers’ pride or with their sisters, while males form coalitions and remain with their partners throughout their lives. This unique behavior sets lions apart from other animals in the animal kingdom.
Frequently Asked Questions On Are Lions Monogamous
Are Lions Loyal To Each Other?
Lions are loyal to their same-sex companions, with females staying in their mothers’ pride or with their sisters, while males remain with their coalition partners for life. They form temporary bonds during the mating season but do not mate for life.
Do Lions Mate For Life?
Lions do not mate for life, but they form temporary bonds during mating season. Male and female lions venture out to hunt and provide for their young. While not monogamous, lions display strong social bonds and care for their partners and offspring.
Do Lions Actually Love Their Mates?
Yes, lions show strong social bonds and care for their partners and offspring, indicating a form of affection. Females stay with their mothers or sisters, while males remain with their coalition partners for life. However, the concept of love may not be directly applicable to animals like it is to humans.
Why Do Lions Mate So Many Times Female?
Lionesses mate with multiple males to increase chances of successful fertilization and discourage infanticide.
Conclusion
Lions may not be monogamous, but they do form strong social bonds and display loyalty towards their like-sexed companions. Females stay with their mothers’ pride or sisters in a new pride, while males remain with their coalition partners throughout their lives.
Though not monogamous in the traditional sense, lions exhibit behaviors that indicate strong social connections and care for their partners and offspring. Understanding the dynamics of lion relationships adds to our knowledge of these fascinating creatures.