How Big Do Elephant Trunk Snakes Get
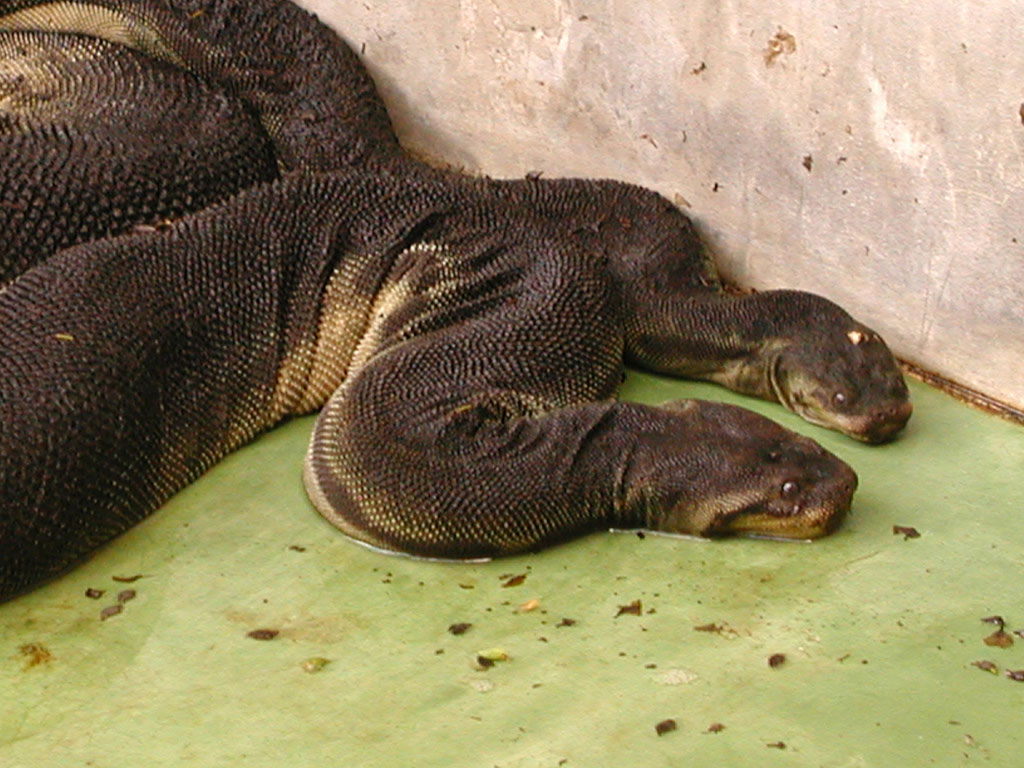

The Elephant Trunk Snake can reach an average adult size of five to eight feet. Known for their unique appearance, these aquatic snakes resemble an elephant’s trunk and have the ability to live underwater.
Elephant Trunk Snakes are carnivores and primarily feed on fish and amphibians such as frogs. They do not seem to have a fish preference and can also consume dead fish. These snakes can be kept in tanks with live feeder fish to provide a constant supply of food.
Despite their intimidating size, Elephant Trunk Snakes are non-venomous and pose no threat to humans.

Credit: thlpp.tumblr.com
Physical Characteristics Of Elephant Trunk Snakes
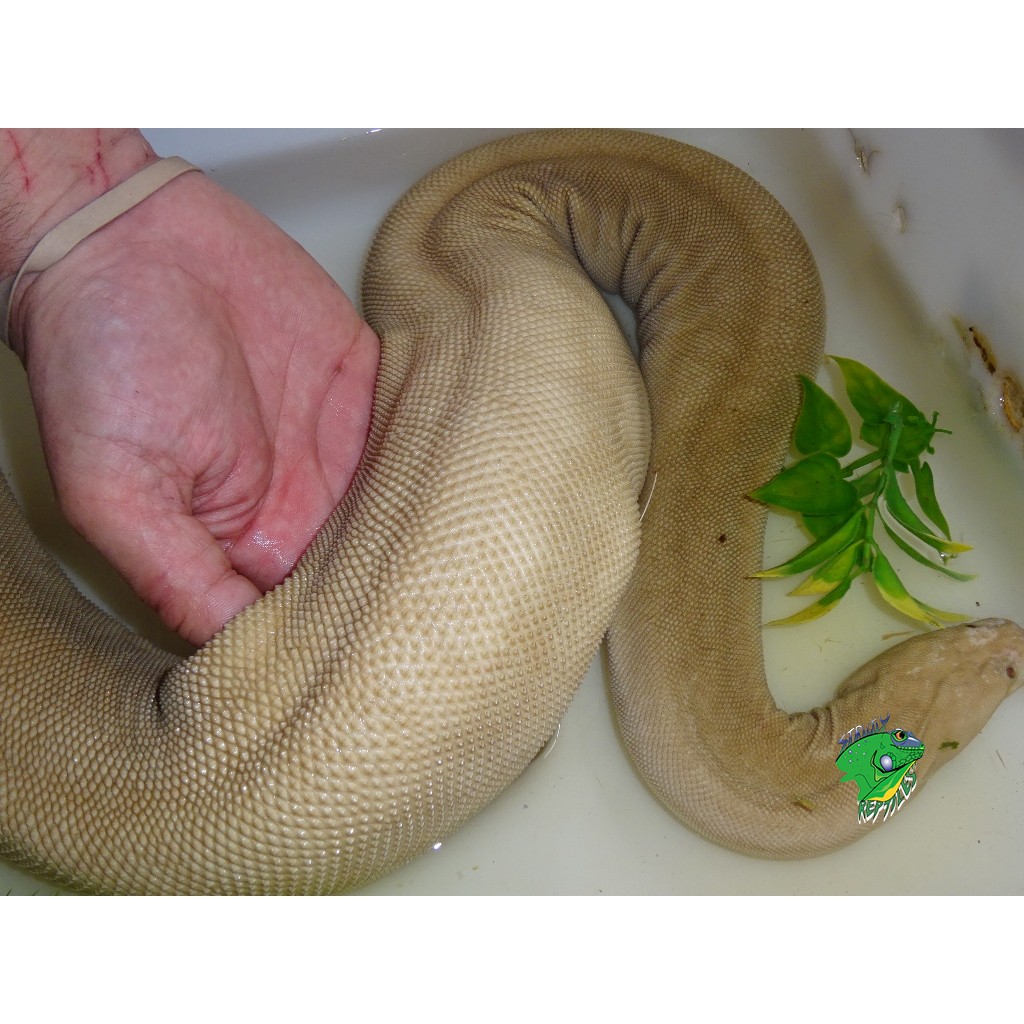
Elephant Trunk Snakes, also known as Acrochordus javanicus, are a species of snake that possess unique physical characteristics. Size: These semi-aquatic creatures can reach lengths of over two meters, making them one of the largest aquatic snakes. Appearance: Their long and slender bodies, with distinctively wrinkled skin, resemble the trunk of an elephant, hence their name. With no venom, these non-aggressive snakes feed on fish and amphibians. While they can be kept as pets, they require specific care due to their aquatic nature. Their unmistakable resemblance to an elephant’s trunk and their intriguing lifestyle make them a unique addition to the world of reptiles.
Habitat And Distribution
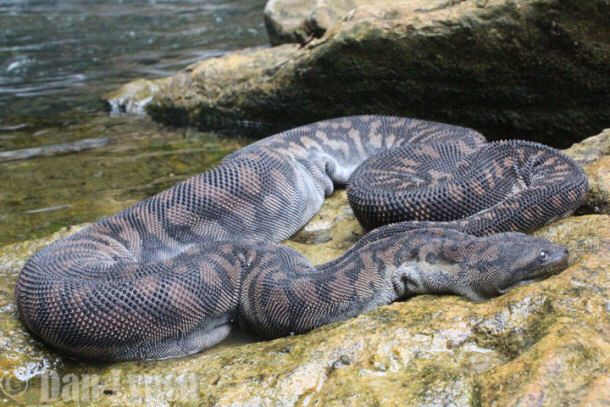
The Elephant Trunk Snake (Acrochordus javanicus) can reach lengths of over two meters, making it one of the larger aquatic snakes. Known for its unique appearance resembling an elephant’s trunk, it is a non-venomous species that primarily feeds on fish and amphibians.
Its distribution includes various habitats such as rivers, swamps, and mangrove forests.
Freshwater Habitats
The Elephant Trunk Snake (Acrochordus javanicus) is a non-venomous aquatic snake that inhabits freshwater habitats. These snakes can be found in various freshwater ecosystems, including rivers, lakes, swamps, and ponds. They are adapted to living in these habitats and have specific characteristics that allow them to thrive in these environments.
The geographical range of Elephant Trunk Snakes is quite extensive. They are found in Southeast Asia, including countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and the Philippines. These snakes also inhabit parts of Australia and New Guinea. Their distribution is mainly limited to these regions.
Elephant Trunk Snakes primarily feed on fish and amphibians, such as frogs, in their freshwater habitats. They are carnivores and have no particular preference for a specific type of fish. Some individuals may take dead fish as food, but others prefer live feeder fish.
These snakes have a unique appearance, with a long and cylindrical body, and a head that resembles an elephant’s trunk. Hence, their name. Their forked tongue and ability to breathe air allow them to live underwater and explore their aquatic habitats.
Elephant Trunk Snakes can grow up to two meters in length, making them quite large snakes. They are not commonly kept as pets due to their specialized habitat requirements. These snakes are well-adapted to their freshwater environments, avoiding open water and staying cautious of predators from above.
Diet And Feeding Habits
Diet: These carnivores feed on fish and amphibians, such as frogs. They don’t seem to have a fish preference. Some will take dead fish, but only some. Live feeder fish can be maintained in the tank for a constant supply of food.
According to Reptiles Magazine, the Elephant Trunk Snake (Acrochordus javanicus) is a non-venomous aquatic snake that belongs to the family Acrochordidae. These snakes are primitive and non-poisonous.
The Elephant Trunk Snake gets its name due to its resemblance to an elephant’s trunk. However, it is important to note that this snake has a forked tongue and lives underwater.
This unique creature is not adapted for breathing air, but instead relies on gills for respiration.
Overall, the diet and feeding habits of Elephant Trunk Snakes primarily revolve around their carnivorous nature and their preference for fish and amphibians as their main source of food.

Credit: www.floridamuseum.ufl.edu
Trivia And Fun Facts
Trivia and Fun Facts about Elephant Trunk Snakes:
Why the Name Elephant Trunk Snake? The Elephant Trunk Snake is named after its long snout that resembles an elephant’s trunk.
Ability to Breathe Air: Despite being primarily aquatic, Elephant Trunk Snakes are air-breathing and need to surface to breathe.
These non-venomous aquatic snakes primarily feed on fish and amphibians, such as frogs, and are known for their unique appearance resembling an elephant’s trunk.
Credit: strictlyreptiles.tv
Frequently Asked Questions On How Big Do Elephant Trunk Snakes Get
What Do Elephant Trunk Snakes Eat?
Elephant trunk snakes are carnivores that primarily eat fish and amphibians, like frogs. They can also consume dead fish and live feeder fish for a constant food supply. Their diet does not seem to have a preference for specific types of fish.
Is Elephant Trunk Snake Poisonous?
The Elephant Trunk Snake is non-venomous, therefore it is not poisonous to humans or animals.
Why Is It Called Elephant Trunk Snake?
The Elephant Trunk Snake is named after its resemblance to an elephant’s trunk, even though it’s a snake that lives underwater.
Do Elephant Trunk Snakes Breathe Air?
Elephant trunk snakes do breathe air as they are amphibious creatures and have lungs.
Conclusion
The Elephant Trunk Snake is a fascinating and unique creature for reptile enthusiasts. With an ability to reach an average adult size of five to eight feet, they are truly impressive. Their aquatic lifestyle and feeding habits make them a truly captivating species to learn about and interact with.
If you are considering owning an Elephant Trunk Snake, it is essential to understand their specific needs and behavior to provide a suitable environment for their well-being.





